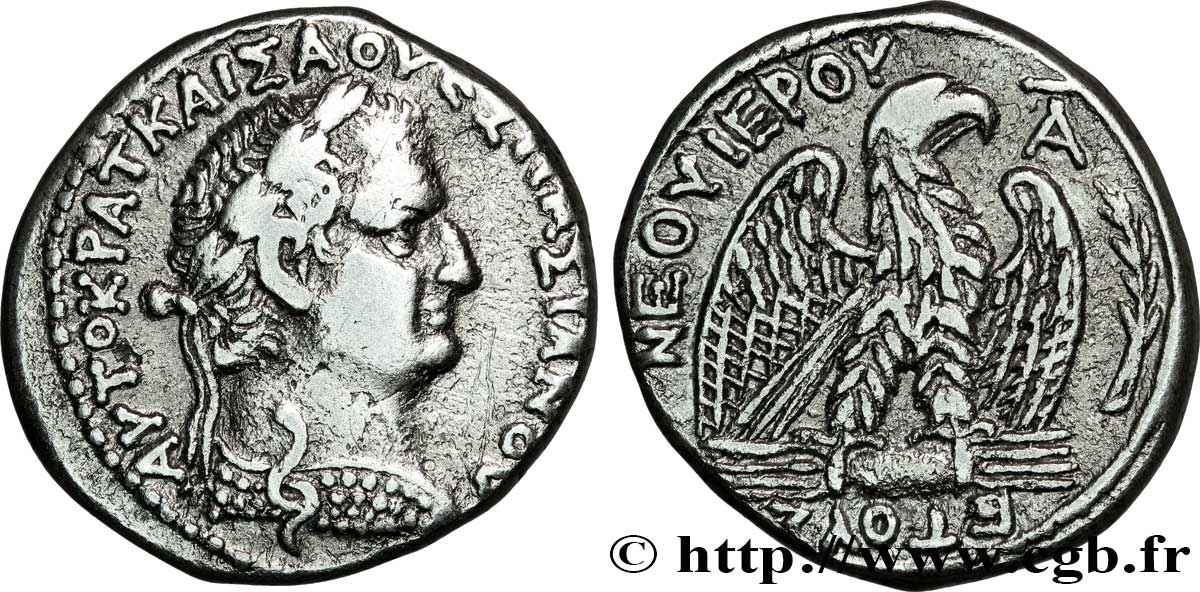
bpv_304488 - VESPASIANO Tétradrachme syro-phénicien
non disponibile.
Articolo venduto sul nostro negozio (2014)
Prezzo : 380.00 €
Articolo venduto sul nostro negozio (2014)
Prezzo : 380.00 €
Tipo : Tétradrachme syro-phénicien
Data: an 2
Nome della officina / città: Antioche, Syrie, Séleucie et Piérie
Metallo : argento
Diametro : 26 mm
Asse di coniazione : 11 h.
Peso : 14,86 g.
Grado di rarità : R2
N° nelle opere di riferimento :
Pedigree :
Cet exemplaire, qui provient de la Collection McAlee, illustre le type dans le livre Coins of Roman Antioch, c’est l’exemplaire 0103_007 de la base TSP
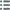
Diritto
Descrittivo diritto : Tête laurée de Vespasien à droite, aegis ancienne autour du cou (O*4).
Legenda diritto : AUTOKRAT KAISA OUESPASIANOU
Traduzione diritto : (L'empereur césar Vespasien).
Rovescio
Descrittivo rovescio : Aigle, ailes écartées, à droite sur un foudre, palme verticale dans le champ droit.
Legenda rovescio : ETOUS NEOU IEROU A
Traduzione rovescio : (Nouvelle année sainte An 1).
Commento
Curieusement, ce qui se rapproche le plus de ces émissions du premier groupe de Vespasien, fort rare, caractérisé par un aigle sur foudre à droite, ce sont aussi bien les émissions du milieu du règne de Néron (Prieur 84 à 89), de dix ans antérieures, que les premières émissions du règne de Domitien. (Prieur 143). Faut-il en déduire qu’il était politique à Antioche, pour un nouvel empereur du premier siècle, de rappeler le souvenir de ces frappes de Néron ? L’aegis si particulière qui les caractérise (dite ancienne et se composant apparemment d’une peau de chèvre et d’un serpent, sans rapport direct avec l’aegis normale, ornement de poitrine rappelant la Méduse) avait-elle une signification particulière pour les Antiochéens ? Si tel est le cas, son identification, si elle peut être confirmée, renvoie au culte de Zeus, comme l’aigle et le foudre. Pourtant, le principal culte d’Antioche semble avoir été dédié à Apollon...
Ce premier groupe, placé là d’une manière arbitraire (il comporte les années A et B, mais comme les groupes 5, 6 et 9), n’a aucun rapport avec les émissions de Galba et d’Othon : faut-il en déduire qu’il n’a pas été frappé à Antioche ou que les frappes de ceux-ci émanent d’une autre ville ? La question reste encore posée. On remarque par ailleurs que les aigles de ce groupe ne portent pas la couronne dans le bec, probablement une distinction accordée à la ville émettrice.
Le premier groupe se termine en l’an 2, numériquement, c’est l’un des plus réduits de l’ample production liée à la guerre Juive.
Les sigma sont traités en C.
Dans la base TSP maintenue par Michel Prieur, treize exemplaires seulement sont maintenant répertoriés.
Curiously, what comes closest to these issues of the first group of Vespasian, very rare, characterized by an eagle on a thunderbolt on the right, are both the issues from the middle of the reign of Nero (Prior 84 to 89), from ten years earlier, and the first issues of the reign of Domitian.. (Prior 143). Should we deduce from this that it was political in Antioch, for a new emperor of the first century, to recall the memory of these strikes of Nero? Did the very particular aegis which characterizes them (said to be ancient and apparently consisting of a goatskin and a snake, without direct relation to the normal aegis, a chest ornament reminiscent of Medusa) have a particular significance for the Antiochians? If this is the case, its identification, if it can be confirmed, refers to the cult of Zeus, like the eagle and the thunderbolt. Yet the main cult of Antioch seems to have been dedicated to Apollo. . .
This first group, placed there arbitrarily (it includes years A and B, but like groups 5, 6 and 9), has no connection with the issues of Galba and Otho: should we deduce from this that it was not struck in Antioch or that the strikes of these came from another city? The question still remains.. It is also noted that the eagles in this group do not wear the crown in their beaks, probably a distinction granted to the issuing city..
The first group ends in the year 2, numerically, it is one of the smallest of the large production linked to the Jewish War.
Sigmas are treated in C.
In the TSP database maintained by Michel Prieur, only thirteen examples are now listed.
Ce premier groupe, placé là d’une manière arbitraire (il comporte les années A et B, mais comme les groupes 5, 6 et 9), n’a aucun rapport avec les émissions de Galba et d’Othon : faut-il en déduire qu’il n’a pas été frappé à Antioche ou que les frappes de ceux-ci émanent d’une autre ville ? La question reste encore posée. On remarque par ailleurs que les aigles de ce groupe ne portent pas la couronne dans le bec, probablement une distinction accordée à la ville émettrice.
Le premier groupe se termine en l’an 2, numériquement, c’est l’un des plus réduits de l’ample production liée à la guerre Juive.
Les sigma sont traités en C.
Dans la base TSP maintenue par Michel Prieur, treize exemplaires seulement sont maintenant répertoriés.
Curiously, what comes closest to these issues of the first group of Vespasian, very rare, characterized by an eagle on a thunderbolt on the right, are both the issues from the middle of the reign of Nero (Prior 84 to 89), from ten years earlier, and the first issues of the reign of Domitian.. (Prior 143). Should we deduce from this that it was political in Antioch, for a new emperor of the first century, to recall the memory of these strikes of Nero? Did the very particular aegis which characterizes them (said to be ancient and apparently consisting of a goatskin and a snake, without direct relation to the normal aegis, a chest ornament reminiscent of Medusa) have a particular significance for the Antiochians? If this is the case, its identification, if it can be confirmed, refers to the cult of Zeus, like the eagle and the thunderbolt. Yet the main cult of Antioch seems to have been dedicated to Apollo. . .
This first group, placed there arbitrarily (it includes years A and B, but like groups 5, 6 and 9), has no connection with the issues of Galba and Otho: should we deduce from this that it was not struck in Antioch or that the strikes of these came from another city? The question still remains.. It is also noted that the eagles in this group do not wear the crown in their beaks, probably a distinction granted to the issuing city..
The first group ends in the year 2, numerically, it is one of the smallest of the large production linked to the Jewish War.
Sigmas are treated in C.
In the TSP database maintained by Michel Prieur, only thirteen examples are now listed.








 Segnalare un errore
Segnalare un errore Stampate la pagina
Stampate la pagina Condividi mia selezione
Condividi mia selezione Fai una domanda
Fai una domanda Consegnare / vendere
Consegnare / vendere
 Descrittivo
Descrittivo















