fme_1086679 - TERZA REPUBBLICA FRANCESE Médaille, Exposition Universelle
80.00 €
Quantità
Aggiungi al carrello

Tipo : Médaille, Exposition Universelle
Data: 1900
Nome della officina / città: Paris
Metallo : bronzo argentato
Diametro : 37 mm
Asse di coniazione : 12 h.
Peso : 14,37 g.
Orlo : lisse
Marchio : sans poinçon
Grado di rarità : R2
Commenti sullo stato di conservazione:
Patine hétérogène avec des traces d’usure et rayures. Taches d’oxydation. Argenture partie notamment sur la tranche
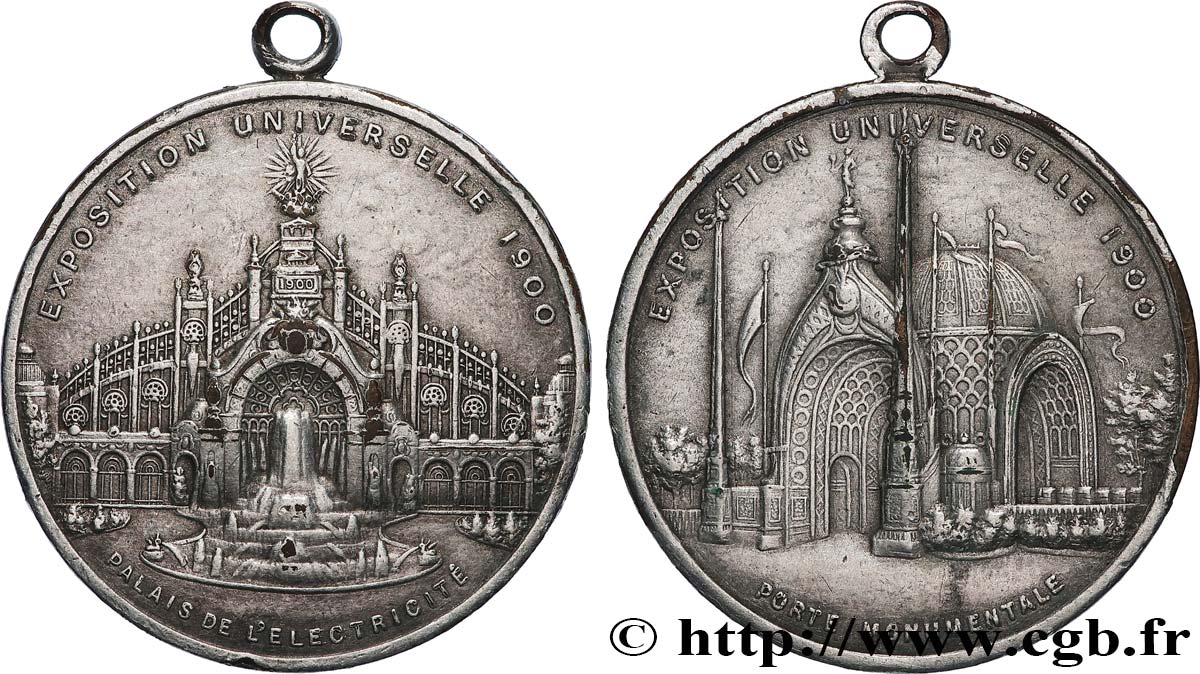
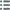
Diritto
Titolatura diritto : EXPOSITION UNIVERSELLE 1900 / PALAIS DE L’ELECTRICITE.
Descrittivo diritto : Le palais de l’électricité.
Rovescio
Titolatura rovescio : EXPOSITION UNIVERSELLE 1900 / PORTE MONUMENTALE.
Descrittivo rovescio : La porte du palais de l’électricité.
Commento
Médaille avec un diamètre sans bélière de 33 mm
Jeux et Exposition Universelle se superposèrent. L'Exposition Universelle s'est tenue du 14 avril au 12 novembre 1900 avec plus de 50 millions de visiteurs et 83.000 exposants.
Les expositions universelles ont été créées pour présenter les réalisations industrielles des différentes nations. Elles représentaient la vitrine technologique et industrielle des participants, témoignant du progrès au cours de la révolution industrielle. La première exposition universelle s'est déroulée à Londres en 1851.
À l'origine, chaque pays disposait d'un espace réservé dans un pavillon central. À partir de 1867, des pavillons nationaux firent leur apparition. En principe, ils étaient attribués seulement s'il y avait des choses à présenter que le pavillon central ne pouvait accueillir. Ils ne tardèrent pas à se généraliser, les nations exposantes construisant des pavillons typiques de l'architecture de leurs pays.
La compétition était omniprésente dans les expositions universelles, et des concours permettaient aux plus méritants d'obtenir des médailles bénéficiant d'un certain prestige.
De nombreuses réalisations architecturales construites à l'occasion d'expositions universelles sont devenues par la suite des symboles des villes qui les ont abritées : la tour Eiffel à Paris, l'Atomium à Bruxelles, le Space Needle à Seattle, la Biosphère à Montréal.
Enfin, la tenue des expositions universelles a toujours été l'occasion de mettre en place des projets d'urbanisme : construction du métro de Paris en 1900 ou celui de Montréal en 1967, extension du métro de Lisbonne en 1998…
Voir http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exposition_universelle .
Medal with a diameter of 33 mm without the bail. The Games and the Universal Exhibition overlapped.. The Universal Exhibition was held from April 14 to November 12, 1900, with over 50 million visitors and 83. 000 exhibitors.
World's fairs were created to showcase the industrial achievements of different nations.. They represented the technological and industrial showcase of the participants, bearing witness to the progress made during the industrial revolution.. The first World's Fair took place in London in 1851..
Originally, each country had its own reserved space in a central pavilion.. From 1867 onwards, national pavilions began to appear.. In principle, they were only allocated if there were things to display that the central pavilion could not accommodate.. They soon became widespread, with exhibiting nations building pavilions typical of their countries' architecture..
Competition was omnipresent at world's fairs, and contests allowed the most deserving to obtain medals that carried a certain prestige..
Many architectural achievements built for world's fairs have subsequently become symbols of the cities that hosted them: the Eiffel Tower in Paris, the Atomium in Brussels, the Space Needle in Seattle, the Biosphere in Montreal.
Finally, the holding of world's fairs has always been an opportunity to implement urban planning projects: the construction of the Paris metro in 1900 or that of Montreal in 1967, the extension of the Lisbon metro in 1998… See http://fr. Wikipedia. org/wiki/Exposition_universelle
Jeux et Exposition Universelle se superposèrent. L'Exposition Universelle s'est tenue du 14 avril au 12 novembre 1900 avec plus de 50 millions de visiteurs et 83.000 exposants.
Les expositions universelles ont été créées pour présenter les réalisations industrielles des différentes nations. Elles représentaient la vitrine technologique et industrielle des participants, témoignant du progrès au cours de la révolution industrielle. La première exposition universelle s'est déroulée à Londres en 1851.
À l'origine, chaque pays disposait d'un espace réservé dans un pavillon central. À partir de 1867, des pavillons nationaux firent leur apparition. En principe, ils étaient attribués seulement s'il y avait des choses à présenter que le pavillon central ne pouvait accueillir. Ils ne tardèrent pas à se généraliser, les nations exposantes construisant des pavillons typiques de l'architecture de leurs pays.
La compétition était omniprésente dans les expositions universelles, et des concours permettaient aux plus méritants d'obtenir des médailles bénéficiant d'un certain prestige.
De nombreuses réalisations architecturales construites à l'occasion d'expositions universelles sont devenues par la suite des symboles des villes qui les ont abritées : la tour Eiffel à Paris, l'Atomium à Bruxelles, le Space Needle à Seattle, la Biosphère à Montréal.
Enfin, la tenue des expositions universelles a toujours été l'occasion de mettre en place des projets d'urbanisme : construction du métro de Paris en 1900 ou celui de Montréal en 1967, extension du métro de Lisbonne en 1998…
Voir http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exposition_universelle .
Medal with a diameter of 33 mm without the bail. The Games and the Universal Exhibition overlapped.. The Universal Exhibition was held from April 14 to November 12, 1900, with over 50 million visitors and 83. 000 exhibitors.
World's fairs were created to showcase the industrial achievements of different nations.. They represented the technological and industrial showcase of the participants, bearing witness to the progress made during the industrial revolution.. The first World's Fair took place in London in 1851..
Originally, each country had its own reserved space in a central pavilion.. From 1867 onwards, national pavilions began to appear.. In principle, they were only allocated if there were things to display that the central pavilion could not accommodate.. They soon became widespread, with exhibiting nations building pavilions typical of their countries' architecture..
Competition was omnipresent at world's fairs, and contests allowed the most deserving to obtain medals that carried a certain prestige..
Many architectural achievements built for world's fairs have subsequently become symbols of the cities that hosted them: the Eiffel Tower in Paris, the Atomium in Brussels, the Space Needle in Seattle, the Biosphere in Montreal.
Finally, the holding of world's fairs has always been an opportunity to implement urban planning projects: the construction of the Paris metro in 1900 or that of Montreal in 1967, the extension of the Lisbon metro in 1998… See http://fr. Wikipedia. org/wiki/Exposition_universelle








 Segnalare un errore
Segnalare un errore Stampate la pagina
Stampate la pagina Condividi mia selezione
Condividi mia selezione Fai una domanda
Fai una domanda Consegnare / vendere
Consegnare / vendere
 Descrittivo
Descrittivo















