fwo_563444 - OMEYYADES - HASHIM Dinar d’or 736 Syrie, Damas
non disponibile.
Articolo venduto sul nostro negozio (2019)
Prezzo : 800.00 €
Articolo venduto sul nostro negozio (2019)
Prezzo : 800.00 €
Tipo : Dinar d’or
Data: AH. 118
Data: 736
Nome della officina / città: Syrie, Damas
Metallo : oro
Titolo in millesimi : 1000 ‰
Diametro : 20 mm
Asse di coniazione : 6 h.
Peso : 4,24 g.
Grado di rarità : R1
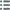
Diritto
Descrittivo diritto : Légende circulaire ; au centre, légende en trois lignes.
Rovescio
Descrittivo rovescio : Légende circulaire ; au centre légende en trois lignes.
Commento
Le nom du dinar vient, par le Syriaque, de denarius aureus (denier d'or). Créé en 696-697 (an 77 de l'Hégire) par le calife Abd el Malik, il a pour modèle le solidus byzantin. Longtemps frappé uniquement à Damas, la capitale, il est alors inutile d'indiquer l'atelier sur les pièces. La masse choisie, 4,25 grammes environ, est fondée sur la masse arabe d'un metqäl, mais correspond en même temps à la moyenne des masses d'un assez grand nombre de solidi alors en circulation donc un peu usés et n'ayant plus leur masse théorique de 4,5 grammes. D'après la loi dite de Gresham - la mauvaise monnaie chasse la bonne - cette très légère différence devait être un élément favorable à une rapide diffusion du dinar, au détriment du solidus..
The name of the dinar comes, via Syriac, from denarius aureus (gold denarius). Created in 696-697 (year 77 of the Hegira) by the caliph Abd el Malik, it is modeled on the Byzantine solidus. For a long time minted only in Damascus, the capital, it was then unnecessary to indicate the mint on the coins. The chosen mass, approximately 4.25 grams, is based on the Arabic mass of a metqäl, but at the same time corresponds to the average of the masses of a fairly large number of solidi then in circulation, therefore a little worn and no longer having their theoretical mass of 4.5 grams. According to the so-called Gresham's law - bad coin drives out good - this very slight difference was to be a favorable element for a rapid diffusion of the dinar, to the detriment of the solidus.
The name of the dinar comes, via Syriac, from denarius aureus (gold denarius). Created in 696-697 (year 77 of the Hegira) by the caliph Abd el Malik, it is modeled on the Byzantine solidus. For a long time minted only in Damascus, the capital, it was then unnecessary to indicate the mint on the coins. The chosen mass, approximately 4.25 grams, is based on the Arabic mass of a metqäl, but at the same time corresponds to the average of the masses of a fairly large number of solidi then in circulation, therefore a little worn and no longer having their theoretical mass of 4.5 grams. According to the so-called Gresham's law - bad coin drives out good - this very slight difference was to be a favorable element for a rapid diffusion of the dinar, to the detriment of the solidus.








 Segnalare un errore
Segnalare un errore Stampate la pagina
Stampate la pagina Condividi mia selezione
Condividi mia selezione Fai una domanda
Fai una domanda Consegnare / vendere
Consegnare / vendere
 Descrittivo
Descrittivo




