fjt_685811 - EXPOSITIONS DIVERSES LE GENERAL LAFAYETTE 1931
non disponibile.
Articolo venduto sul nostro negozio (2021)
Prezzo : 25.00 €
Articolo venduto sul nostro negozio (2021)
Prezzo : 25.00 €
Tipo : LE GENERAL LAFAYETTE
Data: 1931
Metallo : rame
Diametro : 32 mm
Asse di coniazione : 12 h.
Peso : 18,05 g.
Orlo : lisse
Marchio : corne CUIVRE
Grado di rarità : R1
Commenti sullo stato di conservazione:
Patine marron hétérogène, traces de manipulation. Peu d’usure
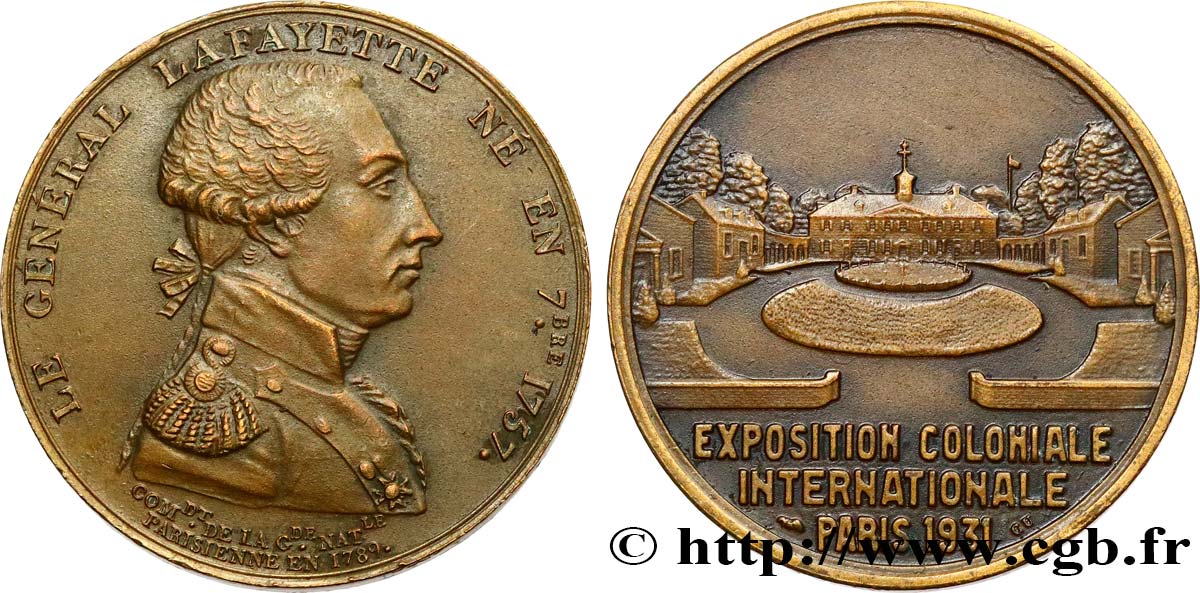
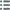
Diritto
Titolatura diritto : LE GENERAL LAFAYETTE NE EN 7BRE 1757 - COMDT. DE LA GDE. NATLE PARISIENNE EN 1789.
Descrittivo diritto : Buste de La Fayette en uniforme à droite.
Rovescio
Titolatura rovescio : 1931 - EXPOSITION COLONIALE INTERNATIONALE DE PARIS.
Descrittivo rovescio : Batiments coloniaux. A l’exergue : corne d’abondance et CU.
Commento
Le droit est repris du fameux jeton de la période révolutionnaire et le revers est commun avec le jeton de l'exposition avec le chef indien. La rareté du modèle de Lafayette, importante, montre un choix net des visiteurs en faveur de l'indien.
La première Exposition Universelle Coloniale générale eut lieu à Paris du 6 mai au 15 novembre 1931. Elle réunissait les colonies des quatre continents : l'Afrique du Nord, l'AOF et l'AEF, Madagascar, les Comores et la Réunion ; l'Amérique avec le Canada et les Iles, la Guyane ; l'Asie avec l'Indochine ; l'Océanie avec la Polynésie. En six mois, il y eut plus de 22,5 millions de visiteurs. L'exposition se déroulait pour la plus grande partie dans le bois de Vincennes et entre la Porte Dorée, la Porte de Saint-Mandé et la Porte de Vincennes. Le clou de l'exposition était la reconstitution du Temple d'Angkor. Il subsiste de cette exposition le musée des Colonies et le zoo de Vincennes.
The obverse is taken from the famous token of the revolutionary period and the reverse is common with the token of the exhibition with the Indian chief. The rarity of the Lafayette model, significant, shows a clear choice of visitors in favor of the Indian. The first general Universal Colonial Exposition took place in Paris from May 6 to November 15, 1931. It brought together the colonies of the four continents: North Africa, French West Africa and French East Africa, Madagascar, the Comoros and Réunion; America with Canada and the Islands, Guyana; Asia with Indochina; Oceania with Polynesia. In six months, there were more than 22.5 million visitors. The exhibition took place for the most part in the Bois de Vincennes and between the Porte Dorée, the Porte de Saint-Mandé and the Porte de Vincennes. The highlight of the exhibition was the reconstruction of the Temple of Angkor. The remains of this exhibition are the Musée des Colonies and the Vincennes Zoo.
La première Exposition Universelle Coloniale générale eut lieu à Paris du 6 mai au 15 novembre 1931. Elle réunissait les colonies des quatre continents : l'Afrique du Nord, l'AOF et l'AEF, Madagascar, les Comores et la Réunion ; l'Amérique avec le Canada et les Iles, la Guyane ; l'Asie avec l'Indochine ; l'Océanie avec la Polynésie. En six mois, il y eut plus de 22,5 millions de visiteurs. L'exposition se déroulait pour la plus grande partie dans le bois de Vincennes et entre la Porte Dorée, la Porte de Saint-Mandé et la Porte de Vincennes. Le clou de l'exposition était la reconstitution du Temple d'Angkor. Il subsiste de cette exposition le musée des Colonies et le zoo de Vincennes.
The obverse is taken from the famous token of the revolutionary period and the reverse is common with the token of the exhibition with the Indian chief. The rarity of the Lafayette model, significant, shows a clear choice of visitors in favor of the Indian. The first general Universal Colonial Exposition took place in Paris from May 6 to November 15, 1931. It brought together the colonies of the four continents: North Africa, French West Africa and French East Africa, Madagascar, the Comoros and Réunion; America with Canada and the Islands, Guyana; Asia with Indochina; Oceania with Polynesia. In six months, there were more than 22.5 million visitors. The exhibition took place for the most part in the Bois de Vincennes and between the Porte Dorée, the Porte de Saint-Mandé and the Porte de Vincennes. The highlight of the exhibition was the reconstruction of the Temple of Angkor. The remains of this exhibition are the Musée des Colonies and the Vincennes Zoo.








 Segnalare un errore
Segnalare un errore Stampate la pagina
Stampate la pagina Condividi mia selezione
Condividi mia selezione Fai una domanda
Fai una domanda Consegnare / vendere
Consegnare / vendere
 Descrittivo
Descrittivo










